How to become pilot in Bangladesh?
 Desk Report
| Published: Saturday, November 22, 2025
Desk Report
| Published: Saturday, November 22, 2025
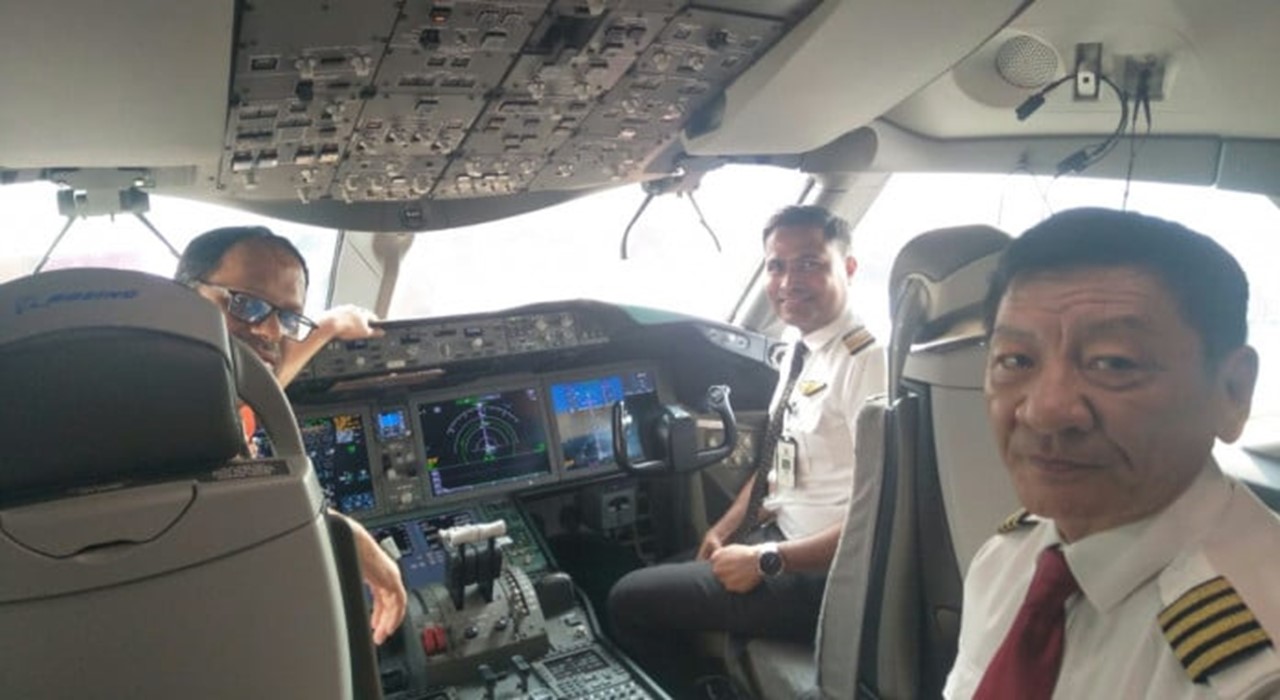

Image: Collected.
Becoming a pilot in Bangladesh is a rewarding but
demanding career path, regulated by the Civil Aviation Authority of Bangladesh
(CAAB). The process involves meeting eligibility criteria, obtaining medical
clearance, completing ground school and flight training at a CAAB-approved
school, and passing exams.
Training can lead to a Private Pilot License
(PPL) for recreational flying or a Commercial Pilot License (CPL) for
professional roles, such as with airlines like Biman Bangladesh Airlines,
US-Bangla Airlines, or Novoair. The entire journey typically takes 12–24 months
for a CPL, depending on weather, scheduling, and your progress. Costs have
risen due to fuel prices but remain more affordable than in many Western
countries.
Many aspiring pilots train
abroad (e.g., USA, Australia) for better facilities and then convert their
license to CAAB standards, as local options can face delays from limited
aircraft and bureaucracy. If you're passionate about military aviation,
consider joining the Bangladesh Air Force (BAF) via their GD(P) entry after
HSC.
Basic eligibility requirements
To start training, you must meet these CAAB-mandated criteria:
|
Requirement |
Details |
|
Age |
Minimum 17 years for Student Pilot
License (SPL) and PPL; 18 years for CPL. No strict upper limit, but airlines
prefer under 35–40 for cadet programs. |
|
Education |
HSC (or equivalent, e.g.,
A-Levels) with at least 60% average marks overall. Science background
(Physics, Chemistry, Math) preferred by most schools, though not always
mandatory—basic math skills suffice. |
|
Medical fitness |
Class 2 Medical Certificate for
SPL/PPL; upgrade to Class 1 for CPL. Exam at CAAB HQ or approved centers
(e.g., vision 6/6, no color blindness, good hearing). Costs ~TK
10,000–20,000. |
|
Language |
Proficient in English (ICAO Level
4+); pass Aviation English Language Proficiency (AELP) test at CAAB. |
|
Other |
Bangladeshi citizen; no criminal
record. For BAF: Unmarried male, height 5'4"+, screened by Inter
Services Selection Board (ISSB). |
Step-by-Step Guide to Becoming a Pilot
- Research and Prepare (1–2 Months) Review CAAB regulations (available on caab.gov.bd).
Decide on PPL (hobby flying) or CPL (professional). If aiming for
airlines, target integrated programs including Instrument Rating (IR) and
Multi-Engine Rating (MER). Join BAF for sponsored training if interested
in military service.
- Obtain Student Pilot License (SPL) Apply at CAAB with HSC certificate, medical proof, and
photos. Valid for 24 months. Cost: ~TK 5,000–10,000. This allows supervised
solo flights.
- Choose a Flight School Enroll in a CAAB-Approved Training Organization (ATO).
Top options:
- Bangladesh Flying Academy (BFA): First CAAB ATO, at Hazrat Shahjalal Intl Airport,
Dhaka. Offers PPL/CPL; 90% of Biman pilots trained here.
- Arirang Flying School: Private school in Dhaka; follows international
standards for PPL/CPL/IR.
- Galaxy Flying Academy: In Rajshahi/Dhaka; residential program with Cessna
fleet; strong on ground classes.
- Biman Airlines Training Centre (BATC): For Biman cadets; EASA-approved, focuses on ATPL.
Other mentions: BAF Shaheen College Flying Club. Compare via school
websites for fleet (e.g., Cessna 152/172) and pass rates.
- Complete Ground School (3–4 Months) Classroom theory: Aerodynamics, navigation,
meteorology, air law. 200–750 hours total for CPL. Held at school or CAAB.
Pass written CAAB exams (e.g., 5 subjects for PPL).
- Flight Training (6–18 Months) Log minimum hours:
- PPL: 40–50 hours (20 solo).
- CPL: 150–200 hours total (including 100 PIC, night
flying, cross-country). Includes simulator time. Weather in Bangladesh
can delay progress. For airlines, add 40–50 hours IR + 10–15 MER.
- Exams and Licensing
- Pass CAAB flight test, oral/practical exams, and Radio
Telephony License (NTC).
- Submit logbook, fees (~TK 20,000–50,000).
- For CPL to ATPL: Gain 1,500 hours experience post-CPL.
- License Conversion (If Trained Abroad) Submit foreign license, flight logs, and exams to CAAB
for equivalency. Process: 1–3 months.
- Job Placement
Apply to airlines (e.g., Biman cadet program requires 60% HSC). Starting
salary: TK 1.5–2 lakh/month; captains earn TK 6–6.5 lakh. Join BAF for
guaranteed income but military commitment.
Costs
(2025 estimates)
Costs vary by school, hours flown,
and extras (e.g., repeats due to failures). Fuel inflation has increased prices
by 20–30% since 2023. Total excludes living expenses (~TK 5–10 lakh/year).
|
License/Program |
Estimated Cost (TK) |
Duration |
Notes |
|
SPL + PPL |
8–12 lakh |
6–8 months |
Basic recreational flying; excludes
multi-engine. |
|
CPL
(Integrated) |
22–30 lakh |
12–18 months |
Includes IR/MER; ~USD 35,000
equivalent. Add 5–10% for exams/uniform. |
|
ATPL Cadet (Biman/BAF) |
10–15 lakh (subsidized) |
18–24 months |
Stipend during training; job guarantee. |
|
Abroad
Training + Conversion |
25–40 lakh |
12–24 months |
USA/Australia cheaper per hour but
visa adds ~TK 2–5 lakh. |
Tips
to Manage Costs: Opt for modular training (PPL
first), train in good weather seasons, or seek airline sponsorships. Avoid
unapproved schools to prevent license issues.
Challenges
and Tips
- Challenges:
Limited local aircraft (delays), high costs, job market saturation (post-COVID
recovery ongoing).
- Tips:
Start with PPL to test interest. Train abroad for modern fleets but budget
for conversion. Network via Reddit (r/Dhaka) or aviation forums. Stay
fit—medical rechecks are annual.
For latest details, visit
caab.gov.bd or contact schools directly.
Make Comment
Login to CommentPopular News
Subscribe to News Letter
Latest News
Weather Outlook
Sunny
Dhaka, Bangladesh
Wind: 8.3 kmph · Precip: 0 mm · Pressure: 1013 mb
17°C
Tue

21.5°C
Wed

21.6°C
Thu

21.3°C















